Deployment Guide
- Preface
- Deployment methods
- Integration with Llama Stack framework
- Local deployment
- Running from container
- Retrieving Lightspeed Core Stack image
- Llama Stack used as a separate process
- Prerequisites
- Installation of all required tools
- Installing dependencies for Llama Stack
- Check if Llama Stack can be started
- Llama Stack configuration
- Run Llama Stack in a separate process
- Lightspeed Core Stack configuration to connect to Llama Stack running in separate process
- Start Lightspeed Core Stack from within a container
- Llama Stack used as a library
- LCS configuration
- Start Lightspeed Core Service from a container
- Usage
Preface
In this document, you will learn how to install and run a service called Lightspeed Core Stack (LCS). It is a service that allows users to communicate with large language models (LLMs), access to RAG databases, call so called agents, process conversation history, ensure that the conversation is only about permitted topics, etc.
Deployment methods
Lightspeed Core Stack (LCS) is built on the Llama Stack framework, which can be run in several modes. Additionally, it is possible to run LCS locally (as a regular Python application) or from within a container. This means that it is possible to leverage multiple deployment methods:
- Local deployment
- Llama Stack framework is used as a library
- Llama Stack framework is used as a separate process (deployed locally)
- Running from a container
- Llama Stack framework is used as a library
- Llama Stack framework is used as a separate process
All those deployments methods will be covered later.
Integration with Llama Stack framework
The Llama Stack framework can be run as a standalone server and accessed via its the REST API. However, instead of direct communication via the REST API (and JSON format), there is an even better alternative. It is based on the so-called Llama Stack Client. It is a library available for Python, Swift, Node.js or Kotlin, which “wraps” the REST API stack in a suitable way, which is easier for many applications.
Llama Stack as a library
When this mode is selected, Llama Stack is used as a regular Python library. This means that the library must be installed in the system Python environment, a user-level environment, or a virtual environment. All calls to Llama Stack are performed via standard function or method calls:
[!NOTE] Even when Llama Stack is used as a library, it still requires the configuration file
run.yamlto be presented. This configuration file is loaded during initialization phase.
Llama Stack as a server
When this mode is selected, Llama Stack is started as a separate REST API service. All communication with Llama Stack is performed via REST API calls, which means that Llama Stack can run on a separate machine if needed.
[!NOTE] The REST API schema and semantics can change at any time, especially before version 1.0.0 is released. By using Lightspeed Core Service, developers, users, and customers stay isolated from these incompatibilities.
Local deployment
In this chapter it will be shown how to run LCS locally. This mode is especially useful for developers, as it is possible to work with the latest versions of source codes, including locally made changes and improvements. And last but not least, it is possible to trace, monitor and debug the entire system from within integrated development environment etc.
Llama Stack used as a separate process
The easiest option is to run Llama Stack in a separate process. This means that there will at least be two running processes involved:
- Llama Stack framework with open port 8321 (can be easily changed if needed)
- LCS with open port 8080 (can be easily changed if needed)
Prerequisites
- Python 3.12 or 3.13
piptool installedjqandcurltools installed
Installation of all required tools
pip install --user uvsudo dnf install curl jq
Installing dependencies for Llama Stack
- Create a new directory outside of the lightspeed-stack project directory
mkdir /tmp/llama-stack-server - Copy the project file named
pyproject.llamastack.tomlinto the new directory, renaming it to `pyproject.toml’:cp examples/pyproject.llamastack.toml /tmp/llama-stack-server/pyproject.toml -
Run the following command to install all llama-stack dependencies in a new venv located in your new directory:
cd /tmp/llama-stack-server uv syncYou should get the following output:
Using CPython 3.12.10 interpreter at: /usr/bin/python3 Creating virtual environment at: .venv Resolved 136 packages in 1.90s Built sqlalchemy==2.0.42 Prepared 14 packages in 10.04s Installed 133 packages in 4.36s + accelerate==1.9.0 + aiohappyeyeballs==2.6.1 ... ... ... + transformers==4.54.0 + triton==3.3.1 + trl==0.20.0 + typing-extensions==4.14.1 + typing-inspection==0.4.1 + tzdata==2025.2 + urllib3==2.5.0 + uvicorn==0.35.0 + wcwidth==0.2.13 + wrapt==1.17.2 + xxhash==3.5.0 + yarl==1.20.1 + zipp==3.23.0
Check if Llama Stack can be started
- In the next step, we need to verify that it is possible to run a tool called
llama. It was installed into a Python virtual environment and therefore we have to run it viauv runcommand:uv run llama - If the installation was successful, the following messages should be displayed on the terminal:
usage: llama [-h] {model,stack,download,verify-download} ... Welcome to the Llama CLI options: -h, --help show this help message and exit subcommands: {model,stack,download,verify-download} model Work with llama models stack Operations for the Llama Stack / Distributions download Download a model from llama.meta.com or Hugging Face Hub verify-download Verify integrity of downloaded model files - If we try to run the Llama Stack without configuring it, only the exception information is displayed (which is not very user-friendly):
uv run llama stack runOutput:
INFO 2025-07-27 16:56:12,464 llama_stack.cli.stack.run:147 server: No image type or image name provided. Assuming environment packages. Traceback (most recent call last): File "/tmp/ramdisk/llama-stack-runner/.venv/bin/llama", line 10, in <module> sys.exit(main()) ^^^^^^ File "/tmp/ramdisk/llama-stack-runner/.venv/lib64/python3.12/site-packages/llama_stack/cli/llama.py", line 53, in main parser.run(args) File "/tmp/ramdisk/llama-stack-runner/.venv/lib64/python3.12/site-packages/llama_stack/cli/llama.py", line 47, in run args.func(args) File "/tmp/ramdisk/llama-stack-runner/.venv/lib64/python3.12/site-packages/llama_stack/cli/stack/run.py", line 164, in _run_stack_run_cmd server_main(server_args) File "/tmp/ramdisk/llama-stack-runner/.venv/lib64/python3.12/site-packages/llama_stack/distribution/server/server.py", line 414, in main elif args.template: ^^^^^^^^^^^^^ AttributeError: 'Namespace' object has no attribute 'template'
Llama Stack configuration
Llama Stack needs to be configured properly. For using the default runnable Llama Stack a file named run.yaml needs to be created. Copy the example examples/run.yaml from the lightspeed-stack project directory into your llama-stack directory.
cp examples/run.yaml /tmp/llama-stack-server
Run Llama Stack in a separate process
- Export OpenAI key by using the following command:
export OPENAI_API_KEY="sk-foo-bar-baz" - Run the following command:
uv run llama stack run run.yaml - Check the output on terminal, it should look like:
INFO 2025-07-29 15:26:20,864 llama_stack.cli.stack.run:126 server: Using run configuration: run.yaml INFO 2025-07-29 15:26:20,877 llama_stack.cli.stack.run:147 server: No image type or image name provided. Assuming environment packages. INFO 2025-07-29 15:26:21,277 llama_stack.distribution.server.server:441 server: Using config file: run.yaml INFO 2025-07-29 15:26:21,279 llama_stack.distribution.server.server:443 server: Run configuration: INFO 2025-07-29 15:26:21,285 llama_stack.distribution.server.server:445 server: apis: - agents - datasetio - eval - inference - post_training - safety - scoring - telemetry - tool_runtime - vector_io benchmarks: [] container_image: null datasets: [] external_providers_dir: null image_name: minimal-viable-llama-stack-configuration inference_store: db_path: .llama/distributions/ollama/inference_store.db type: sqlite logging: null metadata_store: db_path: .llama/distributions/ollama/registry.db namespace: null type: sqlite models: - metadata: {} model_id: gpt-4-turbo model_type: !!python/object/apply:llama_stack.apis.models.models.ModelType - llm provider_id: openai provider_model_id: gpt-4-turbo providers: agents: - config: persistence_store: db_path: .llama/distributions/ollama/agents_store.db namespace: null type: sqlite responses_store: db_path: .llama/distributions/ollama/responses_store.db type: sqlite provider_id: meta-reference provider_type: inline::meta-reference datasetio: - config: kvstore: db_path: .llama/distributions/ollama/huggingface_datasetio.db namespace: null type: sqlite provider_id: huggingface provider_type: remote::huggingface - config: kvstore: db_path: .llama/distributions/ollama/localfs_datasetio.db namespace: null type: sqlite provider_id: localfs provider_type: inline::localfs eval: - config: kvstore: db_path: .llama/distributions/ollama/meta_reference_eval.db namespace: null type: sqlite provider_id: meta-reference provider_type: inline::meta-reference inference: - config: api_key: '********' provider_id: openai provider_type: remote::openai post_training: - config: checkpoint_format: huggingface device: cpu distributed_backend: null provider_id: huggingface provider_type: inline::huggingface safety: - config: excluded_categories: [] provider_id: llama-guard provider_type: inline::llama-guard scoring: - config: {} provider_id: basic provider_type: inline::basic - config: {} provider_id: llm-as-judge provider_type: inline::llm-as-judge - config: openai_api_key: '********' provider_id: braintrust provider_type: inline::braintrust telemetry: - config: service_name: lightspeed-stack sinks: sqlite sqlite_db_path: .llama/distributions/ollama/trace_store.db provider_id: meta-reference provider_type: inline::meta-reference tool_runtime: - config: {} provider_id: model-context-protocol provider_type: remote::model-context-protocol vector_io: - provider_id: faiss provider_type: inline::faiss config: persistence: namespace: vector_io::faiss backend: kv_default storage: backends: kv_default: type: kv_sqlite db_path: .llama/distributions/ollama/kv_store.db scoring_fns: [] server: auth: null host: null port: 8321 quota: null tls_cafile: null tls_certfile: null tls_keyfile: null shields: [] tool_groups: [] vector_stores: [] version: 2 - The server with Llama Stack listens on port 8321. A description of the REST API is available in the form of OpenAPI (endpoint /openapi.json), but other endpoints can also be used. It is possible to check if Llama Stack runs as REST API server by retrieving its version. We use
curlandjqtools for this purposes:curl localhost:8321/v1/version | jq .The output should be in this form:
{ "version": "0.2.22" }
LCS configuration to connect to Llama Stack running in separate process
Copy the examples/lightspeed-stack-lls-external.yaml file to your llama-stack project directory, naming it lightspeed-stack.yaml:
cp examples/lightspeed-stack-lls-external.yaml lightspeed-stack.yaml`
Start LCS
make run
uv run src/lightspeed_stack.py
[07/29/25 15:43:35] INFO Initializing app main.py:19
INFO Including routers main.py:68
INFO: Started server process [1922983]
INFO: Waiting for application startup.
INFO Registering MCP servers main.py:81
DEBUG No MCP servers configured, skipping registration common.py:36
INFO Setting up model metrics main.py:84
[07/29/25 15:43:35] DEBUG Set provider/model configuration for openai/gpt-4-turbo to 0 utils.py:45
INFO App startup complete main.py:86
INFO: Application startup complete.
INFO: Uvicorn running on http://localhost:8080 (Press CTRL+C to quit)
Check if service runs
curl localhost:8080/v1/models | jq .
{
"models": [
{
"identifier": "gpt-4-turbo",
"metadata": {},
"api_model_type": "llm",
"provider_id": "openai",
"type": "model",
"provider_resource_id": "gpt-4-turbo",
"model_type": "llm"
}
]
}
Llama Stack used as a library
It is possible to run Lightspeed Core Stack service with Llama Stack “embedded” as a Python library. This means that just one process will be running and only one port (for example 8080) will be accessible.
Prerequisites
- Python 3.12 or 3.13
piptool installedjqandcurltools installed
Installation of all required tools
pip install --user uvsudo dnf install curl jq
Installing dependencies for Llama Stack
- Clone LCS repository
- Add and install all required dependencies
uv sync --group llslibdev
Llama Stack configuration
Llama Stack needs to be configured properly. Copy the example config from examples/run.yaml to the project directory:
cp examples/run.yaml .
LCS configuration to use Llama Stack in library mode
Copy the example LCS config file from examples/lightspeed-stack-library.yaml to the project directory:
cp examples/lightspeed-stack-lls-library.yaml lightspeed-stack.yaml
Start LCS
- Export OpenAI key by using the following command:
export OPENAI_API_KEY="sk-foo-bar-baz" - Run the following command
make run - Check the output
```text
uv run src/lightspeed_stack.py
Using config run.yaml:
apis:
- agents
- datasetio
- eval
- inference
- post_training
- safety
- scoring
- telemetry
- tool_runtime
- vector_io [07/30/25 20:01:53] INFO Initializing app main.py:19 [07/30/25 20:01:54] INFO Including routers main.py:68 INFO Registering MCP servers main.py:81 DEBUG No MCP servers configured, skipping registration common.py:36 INFO Setting up model metrics main.py:84 [07/30/25 20:01:54] DEBUG Set provider/model configuration for openai/openai/chatgpt-4o-latest to 0 utils.py:45 DEBUG Set provider/model configuration for openai/openai/gpt-3.5-turbo to 0 utils.py:45 DEBUG Set provider/model configuration for openai/openai/gpt-3.5-turbo-0125 to 0 utils.py:45 DEBUG Set provider/model configuration for openai/openai/gpt-3.5-turbo-instruct to 0 utils.py:45 DEBUG Set provider/model configuration for openai/openai/gpt-4 to 0 utils.py:45 DEBUG Set provider/model configuration for openai/openai/gpt-4-turbo to 0 utils.py:45 DEBUG Set provider/model configuration for openai/openai/gpt-4o to 0 utils.py:45 DEBUG Set provider/model configuration for openai/openai/gpt-4o-2024-08-06 to 0 utils.py:45 DEBUG Set provider/model configuration for openai/openai/gpt-4o-audio-preview to 0 utils.py:45 DEBUG Set provider/model configuration for openai/openai/gpt-4o-mini to 0 utils.py:45 DEBUG Set provider/model configuration for openai/openai/o1 to 0 utils.py:45 DEBUG Set provider/model configuration for openai/openai/o1-mini to 0 utils.py:45 DEBUG Set provider/model configuration for openai/openai/o3-mini to 0 utils.py:45 DEBUG Set provider/model configuration for openai/openai/o4-mini to 0 utils.py:45 DEBUG Set provider/model configuration for openai/openai/text-embedding-3-large to 0 utils.py:45 DEBUG Set provider/model configuration for openai/openai/text-embedding-3-small to 0 utils.py:45 INFO App startup complete main.py:86 ```
Check if service runs
curl localhost:8080/v1/models | jq .
{
"models": [
{
"identifier": "gpt-4-turbo",
"metadata": {},
"api_model_type": "llm",
"provider_id": "openai",
"type": "model",
"provider_resource_id": "gpt-4-turbo",
"model_type": "llm"
}
]
}
Running from container
The image with Lightspeed Core Stack allow users to run the service in two modes. In the first mode, the Llama Stack runs in separate process - in a container or as a local or remote process. Llama Stack functions are accessible via exposed TCP port. In the second model, the Llama Stack is used as a standard Python library which means, that only the Lightspeed Core Stack image is needed and no other packages nor tools need to be installed.
Retrieving Lightspeed Core Stack image
First, it is needed to get an image containing the Lightspeed Core Stack service and all the necessary libraries on which the service depends. It is possible to use the stable release version (like 1.0.0, or “latest” stable), latest development version, or development version identified by a date + SHA (that image is built for any merged pull request).
Prerequisites
podmaninstalled and configured properly
[!NOTE] It is possible to use
dockerinstead ofpodman, but this use case is not tested and thus not supported.
Retrieve the image
Stable release images are tagged with versions like 0.1.0. Tag latest always points to the latest stable release.
Development images are build from main branch every time a new pull request is merged. Image tags for dev images use
the template dev-YYYYMMMDDD-SHORT_SHA e.g. dev-20250704-eaa27fb.
Tag dev-latest always points to the latest dev image built from latest git.
To retrieve the latest dev image, use the following command:
podman pull quay.io/lightspeed-core/lightspeed-stack:dev-latest
It should get the image, copy all layers, and write manifest:
Trying to pull quay.io/lightspeed-core/lightspeed-stack:dev-latest...
Getting image source signatures
Copying blob 455d71b0a12b done |
Copying blob d8e516fe2a03 done |
Copying blob a299c213c55c done |
Copying config 4468f47593 done |
Writing manifest to image destination
4468f475931a54ad1e5c26270ff4c3e55ec31444c1b0bf8fb77a576db7ab33f1
To retrieve stable version 0.2.0, use the following command:
podman pull quay.io/lightspeed-core/lightspeed-stack:0.2.0
Trying to pull quay.io/lightspeed-core/lightspeed-stack:0.2.0...
Getting image source signatures
Copying blob 7c9e86f872c9 done |
Copying blob 455d71b0a12b skipped: already exists
Copying blob a299c213c55c skipped: already exists
Copying config a4982f4319 done |
Writing manifest to image destination
a4982f43195537b9eb1cec510fe6655f245d6d4b7236a4759808115d5d719972
Llama Stack used as a separate process
Lightspeed Core Stack image can run LCS service that connects to Llama Stack running in a separate process. This means that there will at least be two running processes involved:
- Llama Stack framework with open port 8321 (can be easily changed if needed)
- Image with LCS (running in a container) with open port 8080 mapped to local port 8080 (can be easily changed if needed)
[!NOTE] Please note that LCS service will be run in a container. Llama Stack itself can be run in a container, in separate local process, or on external machine. It is just needed to know the URL (including TCP port) to connect to Llama Stack. [!INFO] If Llama Stack is started from a container or is running on separate machine, you can skip next parts - it is expected that everything is setup accordingly.
Prerequisites
- Python 3.12 or 3.13
piptool installedjqandcurltools installed
Installation of all required tools
pip install --user uvsudo dnf install curl jq
Installing dependencies for Llama Stack
- Create a new directory
mkdir llama-stack-server cd llama-stack-server - Create project file named
pyproject.tomlin this directory. This file should have the following content:[project] name = "llama-stack-demo" version = "0.1.0" description = "Default template for PDM package" authors = [] dependencies = [ "llama-stack==0.2.22", "fastapi>=0.115.12", "opentelemetry-sdk>=1.34.0", "opentelemetry-exporter-otlp>=1.34.0", "opentelemetry-instrumentation>=0.55b0", "aiosqlite>=0.21.0", "litellm>=1.72.1", "uvicorn>=0.34.3", "blobfile>=3.0.0", "datasets>=3.6.0", "sqlalchemy>=2.0.41", "faiss-cpu>=1.11.0", "mcp>=1.9.4", "autoevals>=0.0.129", "psutil>=7.0.0", "torch>=2.7.1", "peft>=0.15.2", "trl>=0.18.2"] requires-python = "==3.12.*" readme = "README.md" license = {text = "MIT"} [tool.pdm] distribution = false -
Run the following command to install all dependencies:
uv syncYou should get the following output:
Using CPython 3.12.10 interpreter at: /usr/bin/python3 Creating virtual environment at: .venv Resolved 136 packages in 1.90s Built sqlalchemy==2.0.42 Prepared 14 packages in 10.04s Installed 133 packages in 4.36s + accelerate==1.9.0 + aiohappyeyeballs==2.6.1 ... ... ... + transformers==4.54.0 + triton==3.3.1 + trl==0.20.0 + typing-extensions==4.14.1 + typing-inspection==0.4.1 + tzdata==2025.2 + urllib3==2.5.0 + uvicorn==0.35.0 + wcwidth==0.2.13 + wrapt==1.17.2 + xxhash==3.5.0 + yarl==1.20.1 + zipp==3.23.0
Check if Llama Stack can be started
- In the next step, we need to verify that it is possible to run a tool called
llama. It was installed into a Python virtual environment and therefore we have to run it viauv runcommand:uv run llama - If the installation was successful, the following messages should be displayed on the terminal:
usage: llama [-h] {model,stack,download,verify-download} ... Welcome to the Llama CLI options: -h, --help show this help message and exit subcommands: {model,stack,download,verify-download} model Work with llama models stack Operations for the Llama Stack / Distributions download Download a model from llama.meta.com or Hugging Face Hub verify-download Verify integrity of downloaded model files - If we try to run the Llama Stack without configuring it, only the exception information is displayed (which is not very user-friendly):
uv run llama stack runOutput:
INFO 2025-07-27 16:56:12,464 llama_stack.cli.stack.run:147 server: No image type or image name provided. Assuming environment packages. Traceback (most recent call last): File "/tmp/ramdisk/llama-stack-runner/.venv/bin/llama", line 10, in <module> sys.exit(main()) ^^^^^^ File "/tmp/ramdisk/llama-stack-runner/.venv/lib64/python3.12/site-packages/llama_stack/cli/llama.py", line 53, in main parser.run(args) File "/tmp/ramdisk/llama-stack-runner/.venv/lib64/python3.12/site-packages/llama_stack/cli/llama.py", line 47, in run args.func(args) File "/tmp/ramdisk/llama-stack-runner/.venv/lib64/python3.12/site-packages/llama_stack/cli/stack/run.py", line 164, in _run_stack_run_cmd server_main(server_args) File "/tmp/ramdisk/llama-stack-runner/.venv/lib64/python3.12/site-packages/llama_stack/distribution/server/server.py", line 414, in main elif args.template: ^^^^^^^^^^^^^ AttributeError: 'Namespace' object has no attribute 'template'
Llama Stack configuration
Llama Stack needs to be configured properly. For using the default runnable Llama Stack a file named run.yaml needs to be created. Use the example configuration from examples/run.yaml.
Run Llama Stack in a separate process
- Export OpenAI key by using the following command:
export OPENAI_API_KEY="sk-foo-bar-baz" - Run the following command:
uv run llama stack run run.yaml - Check the output on terminal, it should look like:
INFO 2025-07-29 15:26:20,864 llama_stack.cli.stack.run:126 server: Using run configuration: run.yaml INFO 2025-07-29 15:26:20,877 llama_stack.cli.stack.run:147 server: No image type or image name provided. Assuming environment packages. INFO 2025-07-29 15:26:21,277 llama_stack.distribution.server.server:441 server: Using config file: run.yaml INFO 2025-07-29 15:26:21,279 llama_stack.distribution.server.server:443 server: Run configuration: INFO 2025-07-29 15:26:21,285 llama_stack.distribution.server.server:445 server: apis: - agents - datasetio - eval - inference - post_training - safety - scoring - telemetry - tool_runtime - vector_io benchmarks: [] container_image: null datasets: [] external_providers_dir: null image_name: minimal-viable-llama-stack-configuration inference_store: db_path: .llama/distributions/ollama/inference_store.db type: sqlite logging: null metadata_store: db_path: .llama/distributions/ollama/registry.db namespace: null type: sqlite models: - metadata: {} model_id: gpt-4-turbo model_type: !!python/object/apply:llama_stack.apis.models.models.ModelType - llm provider_id: openai provider_model_id: gpt-4-turbo providers: agents: - config: persistence_store: db_path: .llama/distributions/ollama/agents_store.db namespace: null type: sqlite responses_store: db_path: .llama/distributions/ollama/responses_store.db type: sqlite provider_id: meta-reference provider_type: inline::meta-reference datasetio: - config: kvstore: db_path: .llama/distributions/ollama/huggingface_datasetio.db namespace: null type: sqlite provider_id: huggingface provider_type: remote::huggingface - config: kvstore: db_path: .llama/distributions/ollama/localfs_datasetio.db namespace: null type: sqlite provider_id: localfs provider_type: inline::localfs eval: - config: kvstore: db_path: .llama/distributions/ollama/meta_reference_eval.db namespace: null type: sqlite provider_id: meta-reference provider_type: inline::meta-reference inference: - config: api_key: '********' provider_id: openai provider_type: remote::openai post_training: - config: checkpoint_format: huggingface device: cpu distributed_backend: null provider_id: huggingface provider_type: inline::huggingface safety: - config: excluded_categories: [] provider_id: llama-guard provider_type: inline::llama-guard scoring: - config: {} provider_id: basic provider_type: inline::basic - config: {} provider_id: llm-as-judge provider_type: inline::llm-as-judge - config: openai_api_key: '********' provider_id: braintrust provider_type: inline::braintrust telemetry: - config: service_name: lightspeed-stack sinks: sqlite sqlite_db_path: .llama/distributions/ollama/trace_store.db provider_id: meta-reference provider_type: inline::meta-reference tool_runtime: - config: {} provider_id: model-context-protocol provider_type: remote::model-context-protocol vector_io: - provider_id: faiss provider_type: inline::faiss config: persistence: namespace: vector_io::faiss backend: kv_default storage: backends: kv_default: type: kv_sqlite db_path: .llama/distributions/ollama/kv_store.db scoring_fns: [] server: auth: null host: null port: 8321 quota: null tls_cafile: null tls_certfile: null tls_keyfile: null shields: [] tool_groups: [] vector_stores: [] version: 2 - The server with Llama Stack listens on port 8321. A description of the REST API is available in the form of OpenAPI (endpoint /openapi.json), but other endpoints can also be used. It is possible to check if Llama Stack runs as REST API server by retrieving its version. We use
curlandjqtools for this purposes:curl localhost:8321/v1/version | jq .The output should be in this form:
{ "version": "0.2.22" }
Lightspeed Core Stack configuration to connect to Llama Stack running in separate process
Image with Lightspeed Core Stack needs to be configured properly. Create local file named lightspeed-stack.yaml with the following content:
name: Lightspeed Core Service (LCS)
service:
host: localhost
port: 8080
auth_enabled: false
workers: 1
color_log: true
access_log: true
llama_stack:
use_as_library_client: false
url: http://localhost:8321
api_key: xyzzy
user_data_collection:
feedback_enabled: true
feedback_storage: "/tmp/data/feedback"
transcripts_enabled: true
transcripts_storage: "/tmp/data/transcripts"
authentication:
module: "noop"
Start Lightspeed Core Stack from within a container
Now it is needed to run Lightspeed Core Stack from within a container. The service needs to be configured, so lightspeed-stack.yaml has to be mounted into the container:
podman run -it --network host -v lightspeed-stack.yaml:/app-root/lightspeed-stack.yaml:Z quay.io/lightspeed-core/lightspeed-stack:dev-latest
[!NOTE] Please note that
--network hostis insecure option. It is used there because LCS service running in a container have to access Llama Stack running outside this container and the standard port mapping can not be leveraged there. This configuration would be ok for development purposes, but for real deployment, network needs to be reconfigured accordingly to maintain required container isolation!
Llama Stack used as a library
Llama Stack can be used as a library that is already part of OLS image. It means that no other processed needs to be started, but more configuration is required. Everything will be started from within the one container:
OpenAI key
First, export your OpenAI key into environment variable:
export OPENAI_API_KEY="sk-foo-bar-baz-my-key"
Llama Stack configuration
Create a file named run.yaml. Use the example configuration from examples/run.yaml.
LCS configuration
Create file lightspeed-stack.yaml with the following content:
name: Lightspeed Core Service (LCS)
service:
host: localhost
port: 8080
auth_enabled: false
workers: 1
color_log: true
access_log: true
llama_stack:
use_as_library_client: true
library_client_config_path: ./run.yaml
api_key: xyzzy
user_data_collection:
feedback_enabled: true
feedback_storage: "/tmp/data/feedback"
transcripts_enabled: true
transcripts_storage: "/tmp/data/transcripts"
authentication:
module: "noop"
Start Lightspeed Core Service from a container
Now it is time to start the service from a container. It is needed to mount both configuration files lightspeed-stack.yaml and run.yaml into the container. And it is also needed to expose environment variable containing OpenAI key:
podman run -it -p 8080:8080 -v lightspeed-stack.yaml:/app-root/lightspeed-stack.yaml:Z -v ./run.yaml:/app-root/run.yaml:Z -e OPENAI_API_KEY=${OPENAI_API_KEY} quay.io/lightspeed-core/lightspeed-stack:dev-latest
Usage
The Lightspeed Core Stack service exposes its own REST API endpoints:
Using OpenAPI Swagger UI
Front page
Open http://localhost:8080 URL in your web browser. The following front page should be displayed:

Swagger UI
Click on Swagger UI link to open Swagger UI page:
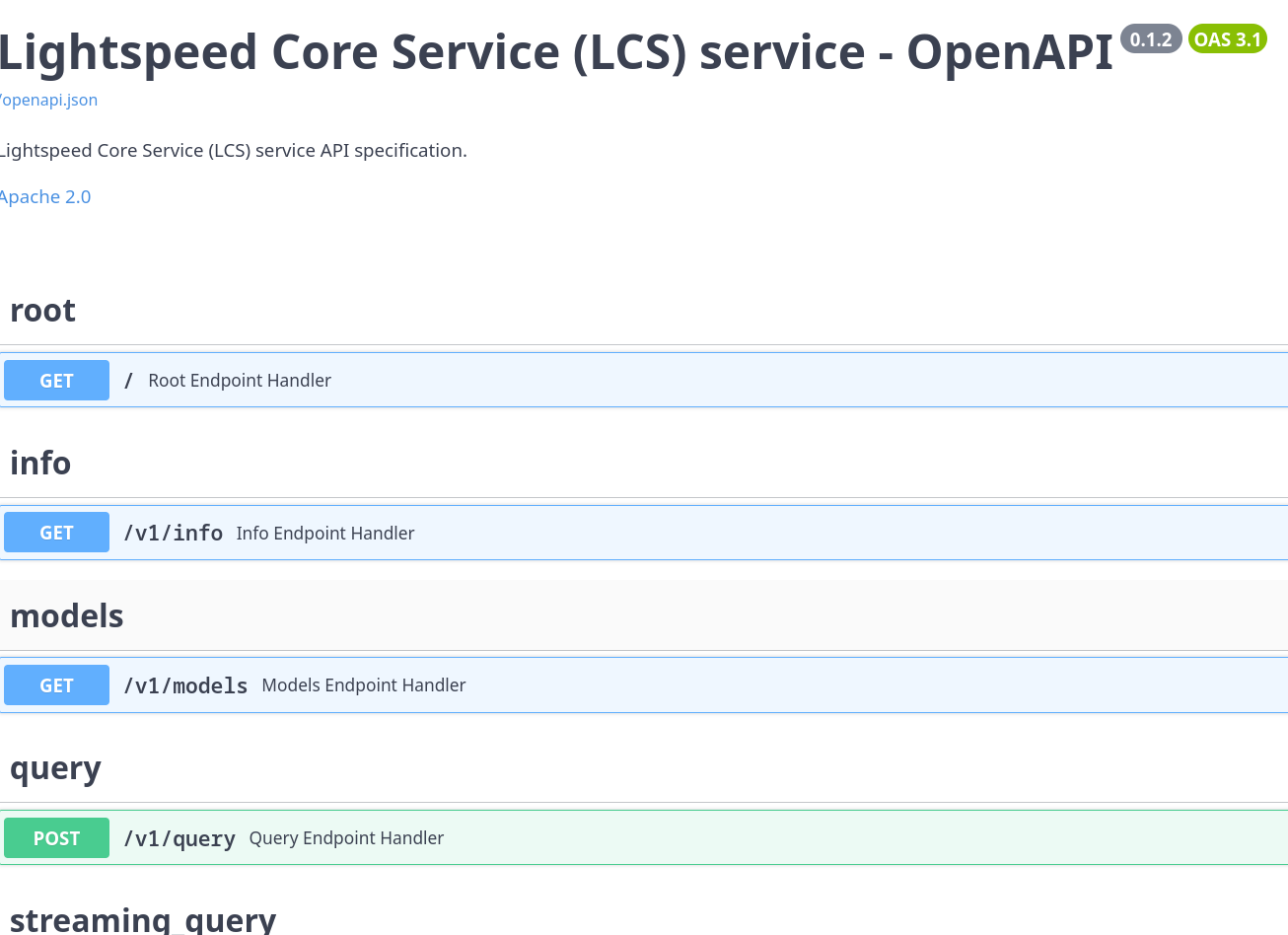
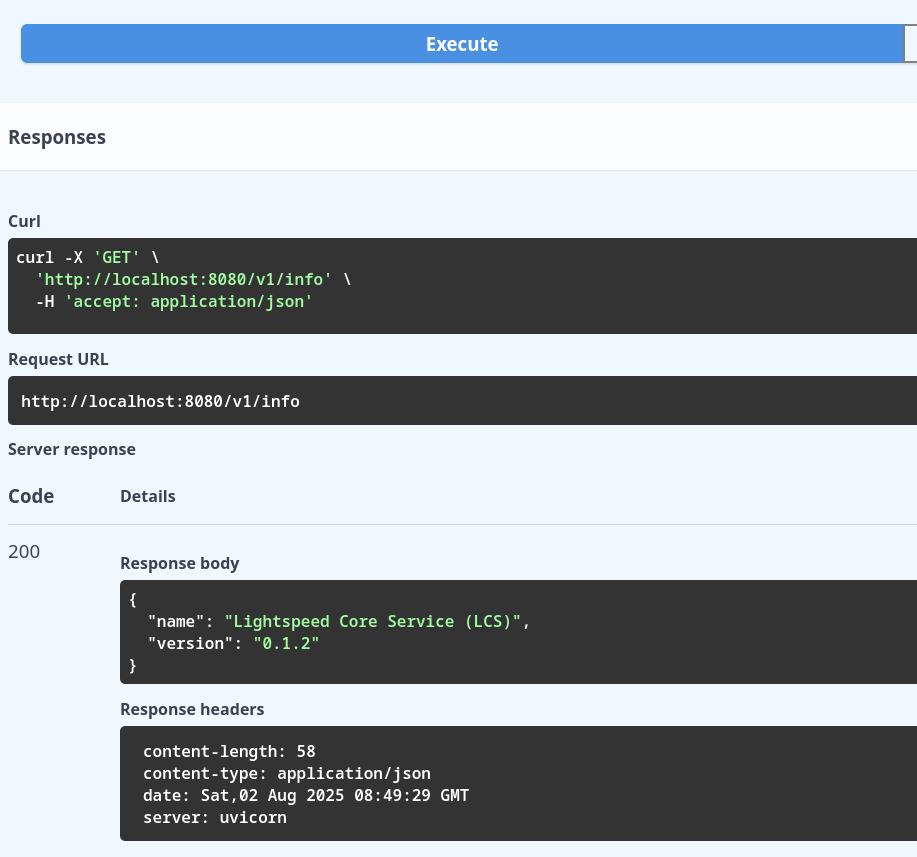
List of all available REST API endpoints is displayed on this page. It is possible to interactively access any endpoint, specify query parameters, JSON payload etc. For example it is possible to access Info endpoint and see actual response from the Lightspeed Core Stack service:
Sending query to LLM
Some REST API endpoints like /query requires payload to be send into the service. This payload should be represented in JSON format. Some attributes in JSON payload are optional, so it is possible to send just the question and system prompt. In this case the JSON payload should look like:

The response retrieved from LLM is displayed directly on Swagger UI page:

Using curl
To access Lightspeed Core Stack service functions via REST API from command line, just the curl tool and optionally jq tool are needed. Any REST API endpoint can be accessed from command line.
Accessing info REST API endpoint
For example, the /v1/info endpoint can be accessed without parameters using HTTP GET method:
curl http://localhost:8080/v1/info | jq .
The response should look like:
{
"name": "Lightspeed Core Service (LCS)",
"version": "0.2.0"
}
Retrieving list of available models
Use the /v1/models to get list of available models:
curl http://localhost:8080/v1/models | jq .
Please note that actual response from the service is larger. It was stripped down in this guide:
{
"models": [
{
"identifier": "gpt-4-turbo",
"metadata": {},
"api_model_type": "llm",
"provider_id": "openai",
"type": "model",
"provider_resource_id": "gpt-4-turbo",
"model_type": "llm"
},
{
"identifier": "openai/gpt-4o-mini",
"metadata": {},
"api_model_type": "llm",
"provider_id": "openai",
"type": "model",
"provider_resource_id": "gpt-4o-mini",
"model_type": "llm"
},
{
"identifier": "openai/gpt-4o-audio-preview",
"metadata": {},
"api_model_type": "llm",
"provider_id": "openai",
"type": "model",
"provider_resource_id": "gpt-4o-audio-preview",
"model_type": "llm"
},
{
"identifier": "openai/chatgpt-4o-latest",
"metadata": {},
"api_model_type": "llm",
"provider_id": "openai",
"type": "model",
"provider_resource_id": "chatgpt-4o-latest",
"model_type": "llm"
},
{
"identifier": "openai/o1",
"metadata": {},
"api_model_type": "llm",
"provider_id": "openai",
"type": "model",
"provider_resource_id": "o1",
"model_type": "llm"
},
{
"identifier": "openai/text-embedding-3-small",
"metadata": {
"embedding_dimension": 1536.0,
"context_length": 8192.0
},
"api_model_type": "llm",
"provider_id": "openai",
"type": "model",
"provider_resource_id": "text-embedding-3-small",
"model_type": "llm"
},
{
"identifier": "openai/text-embedding-3-large",
"metadata": {
"embedding_dimension": 3072.0,
"context_length": 8192.0
},
"api_model_type": "llm",
"provider_id": "openai",
"type": "model",
"provider_resource_id": "text-embedding-3-large",
"model_type": "llm"
}
]
}
Retrieving LLM response
To retrieve LLM response, the question (or query) needs to be send to inference model. Thus the HTTP POST method should be used:
$ curl -X 'POST' \
> 'http://localhost:8080/v1/query' \
> -H 'accept: application/json' \
> -H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
> -d '{
> "query": "write a deployment yaml for the mongodb image",
> "system_prompt": "You are a helpful assistant"
> }'
Response should look like:
{
"conversation_id": "a731eaf2-0935-47ee-9661-2e9b36cda1f4",
"response": "Below is a basic example of a Kubernetes deployment YAML file for deploying a MongoDB instance using the official MongoDB Docker image. This YAML file defines a Deployment resource that manages a Pod with a single MongoDB container.\n\n```yaml\napiVersion: apps/v1\nkind: Deployment\nmetadata:\n name: mongodb-deployment\n labels:\n app: mongodb\nspec:\n replicas: 1\n selector:\n matchLabels:\n app: mongodb\n template:\n metadata:\n labels:\n app: mongodb\n spec:\n containers:\n - name: mongodb\n image: mongo:latest\n ports:\n - containerPort: 27017\n env:\n - name: MONGO_INITDB_ROOT_USERNAME\n value: \"mongoadmin\"\n - name: MONGO_INITDB_ROOT_PASSWORD\n value: \"mongopass\"\n volumeMounts:\n - name: mongodb-data\n mountPath: /data/db\n volumes:\n - name: mongodb-data\n persistentVolumeClaim:\n claimName: mongodb-pvc\n---\napiVersion: v1\nkind: Service\nmetadata:\n name: mongodb-service\nspec:\n ports:\n - port: 27017\n targetPort: 27017\n selector:\n app: mongodb\n type: ClusterIP\n---\napiVersion: v1\nkind: PersistentVolumeClaim\nmetadata:\n name: mongodb-pvc\nspec:\n accessModes:\n - ReadWriteOnce\n resources:\n requests:\n storage: 1Gi\n```\n\n### Explanation of the YAML Components:\n\n1. **Deployment**:\n - `apiVersion: apps/v1`: Specifies the API version for the Deployment.\n - `kind: Deployment`: Specifies that this is a Deployment resource.\n - `metadata`: Metadata about the deployment, such as its name.\n - `spec`: Specification of the deployment.\n - `replicas`: Number of desired pods.\n - `selector`: Selector for pod targeting.\n - `template`: Template for the pod.\n - `containers`: List of containers within the pod.\n - `image`: Docker image of MongoDB.\n - `ports`: Container port MongoDB server listens on.\n - `env`: Environment variables for MongoDB credentials.\n - `volumeMounts`: Mount points for volumes inside the container.\n\n2. **Service**:\n - `apiVersion: v1`: Specifies the API version for the Service.\n - `kind: Service`: Specifies that this is a Service resource.\n - `metadata`: Metadata about the service, such as its name.\n - `spec`: Specification of the service.\n - `ports`: Ports the service exposes.\n - `selector`: Selector for service targeting.\n - `type`: Type of service, `ClusterIP` for internal access.\n\n3. **PersistentVolumeClaim (PVC)**:\n - `apiVersion: v1`: Specifies the API version for the PVC.\n - `kind: PersistentVolumeClaim`: Specifies that this is a PVC resource.\n - `metadata`: Metadata about the PVC, such as its name.\n - `spec`: Specification of the PVC.\n - `accessModes`: Access modes for the volume.\n - `resources`: Resources requests for the volume.\n\nThis setup ensures that MongoDB data persists across pod restarts and provides a basic internal service for accessing MongoDB within the cluster. Adjust the storage size, MongoDB version, and credentials as necessary for your specific requirements."
}
[!NOTE] As is shown on the previous example, the output might contain endlines, Markdown marks etc.